PAPER BATTERY
DEFINITION:
A paper battery is a
flexible, ultra-thin energy storage and production device formed by
combining carbon nanotube s with a conventional sheet of cellulose-based
paper. A paper battery acts as both a high-energy battery and
supercapacitor , combining two components that are separate in
traditional electronics . This combination allows the battery to provide
both long-term, steady power production and bursts of energy.
Non-toxic, flexible paper batteries have the potential to power the next
generation of electronics, medical devices and hybrid vehicles,
allowing for radical new designs and medical technologies.
flexible, ultra-thin energy storage and production device formed by
combining carbon nanotube s with a conventional sheet of cellulose-based
paper. A paper battery acts as both a high-energy battery and
supercapacitor , combining two components that are separate in
traditional electronics . This combination allows the battery to provide
both long-term, steady power production and bursts of energy.
Non-toxic, flexible paper batteries have the potential to power the next
generation of electronics, medical devices and hybrid vehicles,
allowing for radical new designs and medical technologies.
Paper batteries may be folded, cut or
otherwise shaped for different applications without any loss of
integrity or efficiency . Cutting one in half halves its energy
production. Stacking them multiplies power output. Early prototypes of
the device are able to produce 2.5 volt s of electricity from a sample
the size of a postage stam
otherwise shaped for different applications without any loss of
integrity or efficiency . Cutting one in half halves its energy
production. Stacking them multiplies power output. Early prototypes of
the device are able to produce 2.5 volt s of electricity from a sample
the size of a postage stam
Paper battery offers future power:
They have produced a sample slightly
larger than a postage stamp that can store enough energy to illuminate a
small light bulb. But the ambition is to produce reams of paper that
could one day power a car.
larger than a postage stamp that can store enough energy to illuminate a
small light bulb. But the ambition is to produce reams of paper that
could one day power a car.
Professor Robert Linhardt, of the
Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute, said the paper battery was a glimpse
into the future of power storage. The team behind the versatile paper,
which stores energy like a conventional battery, says it can also double
as a capacitor capable of releasing sudden energy bursts for high-power
applications.
Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute, said the paper battery was a glimpse
into the future of power storage. The team behind the versatile paper,
which stores energy like a conventional battery, says it can also double
as a capacitor capable of releasing sudden energy bursts for high-power
applications.
How a paper battery works:
While a conventional battery contains a
number of separate components, the paper battery integrates all of the
battery components in a single structure, making it more energy
efficient.
number of separate components, the paper battery integrates all of the
battery components in a single structure, making it more energy
efficient.
Integrated devices
The research appears in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS).
“Think of all the disadvantages of an
old TV set with tubes,” said Professor Linhardt, from the New York-based
institute, who co-authored a report into the technology.
old TV set with tubes,” said Professor Linhardt, from the New York-based
institute, who co-authored a report into the technology.
“The warm up time, power loss,
component malfunction; you don’t get those problems with integrated
devices. When you transfer power from one component to another you lose
energy. But you lose less energy in an integrated device.”
component malfunction; you don’t get those problems with integrated
devices. When you transfer power from one component to another you lose
energy. But you lose less energy in an integrated device.”
The battery contains carbon nanotubes,
each about one millionth of a centimetre thick, which act as an
electrode. The nanotubes are embedded in a sheet of paper soaked in
ionic liquid electrolytes, which conduct the electricity. The flexible
battery can function even if it is rolled up, folded or cut. Although
the power output is currently modest, Professor Linhardt said that
increasing the output should be easy.
each about one millionth of a centimetre thick, which act as an
electrode. The nanotubes are embedded in a sheet of paper soaked in
ionic liquid electrolytes, which conduct the electricity. The flexible
battery can function even if it is rolled up, folded or cut. Although
the power output is currently modest, Professor Linhardt said that
increasing the output should be easy.
Construction and Structure
Construction
A very brief explanation has been provided.
• Cathode: Carbon Nanotube (CNT)
• Anode: Lithium metal (Li+)
• Electrolyte: All electrolytes (incl. bio electrolytes like blood, sweat and urine)
• Separator: Paper (Cellulose)
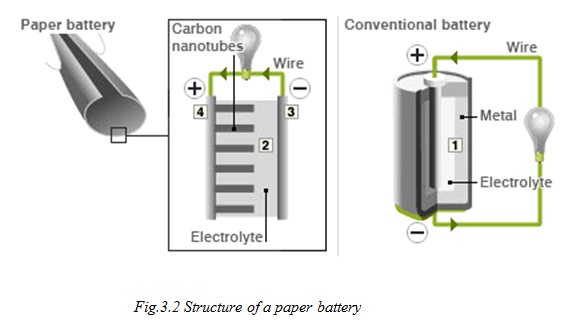
The process of construction can be understood in the following steps:
• Firstly, a common Xerox paper of desired shape and size is taken.
• Next, by conformal coating using a
simple Mayer rod method, the specially formulated ink with suitable
substrates (known as CNT ink) is spread over the paper sample.
simple Mayer rod method, the specially formulated ink with suitable
substrates (known as CNT ink) is spread over the paper sample.
• The strong capillary force in
paper enables high contacting surface area between the paper and
nanotubes after the solvent is absorbed and dried out in an oven.
paper enables high contacting surface area between the paper and
nanotubes after the solvent is absorbed and dried out in an oven.
• A thin lithium film is laminated
over the exposed cellulose surface which completes our paper battery.
This paper battery is then connected to the aluminum current collectors
which connect it to the external load.
over the exposed cellulose surface which completes our paper battery.
This paper battery is then connected to the aluminum current collectors
which connect it to the external load.
• The working of a paper battery is similar to an electrochemical battery except with the constructional differences.
The paper battery is designed to use a
paper-thin sheet of cellulose (which is the major constituent of
regular paper, among other things) infused with aligned carbon
nanotubes. The nanotubes act as electrodes, allowing the storage devices
to conduct electricity. The battery will currently provide a low,
steady power output, as well as a supercapacitor’s quick burst of
energy. While a conventional battery contains a number of separate
components, the paper battery integrates all of the battery components
in a single structure, making it more energy efficient and lighter.
paper-thin sheet of cellulose (which is the major constituent of
regular paper, among other things) infused with aligned carbon
nanotubes. The nanotubes act as electrodes, allowing the storage devices
to conduct electricity. The battery will currently provide a low,
steady power output, as well as a supercapacitor’s quick burst of
energy. While a conventional battery contains a number of separate
components, the paper battery integrates all of the battery components
in a single structure, making it more energy efficient and lighter.