Wireless Charging Of Mobile Phones Using Microwaves
With mobile phones becoming a basic part of life, the recharging
of mobile phone batteries has always been a problem. The mobile phones
vary in their talk time and battery standby according to their
manufacture and batteries. All these phones irrespective of their
manufacturer and batteries have to be put to recharge after the
battery has drained out.
he main objective of this current proposal is to make the
recharging of the mobile phones independent of their manufacturer and
battery make. In this paper a new proposal has been made so as to make
the recharging of the mobile phones is done automatically as you talk in
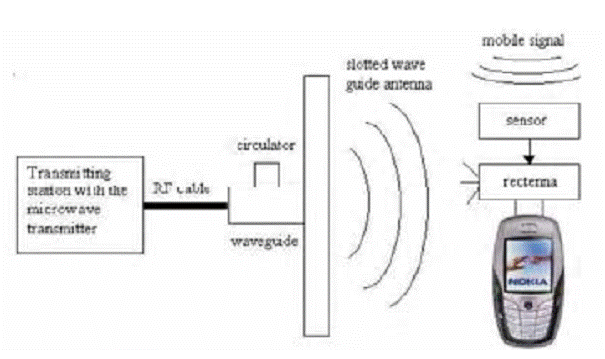
your mobile phone! This is done by use of microwaves. The microwave
signal is transmitted from the transmitter along with the message signal
using special kind of antennas called slotted wave guide antenna at a
frequency is 2.45 GHz.
There are minimal additions, which have to be made in the mobile
handsets, which are the addition of a sensor, a Rectenna, and a filter.
With the above setup, the need for separate chargers for mobile phones
is eliminated and makes charging universal. Thus the more you talk, the
more is your mobile phone charged! With this proposal the manufacturers
would be able to remove the talk time and battery stand by from their
phone specifications.
Wireless Charging Of Mobile Phones Using Microwaves :
The basic addition to the mobile phone is going to be
the rectenna. A rectenna is a rectifying antenna, a special type of
antenna that is used to directly convert microwave energy into DC
electricity.
Its elements are usually arranged in a mesh pattern, giving it a
distinct appearance from most antennae. A simple rectenna can be
constructed from a Schottky diode placed between antenna dipoles. The
diode rectifies the current induced in the antenna by the microwaves.
Rectenna are highly efficient at converting microwave energy to
electricity. In laboratory environments, efficiencies above 90%
have been observed with regularity. Some experimentation has been done
with inverse rectenna, converting electricity into microwave energy, but
efficiencies are much lower–only in the area of 1%. With the advent of
nanotechnology and MEMS the size of these devices can be brought down
to molecular level.
It has been theorized that similar devices, scaled down to the proportions used in
nanotechnology, could be used to convert light into electricity at much
greater efficiencies than what is currently possible with solar cells.
This type of device is called an optical rectenna.
Theoretically, high efficiencies can be maintained as the device
shrinks, but experiments funded by the United States National Renewable
energy Laboratory have so far only obtained roughly 1% efficiency
while using infrared light. Another important part of our
receiver circuitry is a simple sensor.
The basic addition to the mobile phone is going to be the rectenna.
A rectenna is a rectifying antenna, a special type of antenna that is
used to directly convert microwave energy into DC electricity.
Rectifies received microwaves into DC current a rectenna
comprises of a mesh of dipoles and diodes for absorbing microwave energy
from a transmitter and converting it into electric power. Its elements
are usually arranged in a mesh pattern, giving it a distinct appearance
from most antennae. A simple rectenna can be constructed from a Schottky
diode placed between antenna dipoles as shown in Fig…
The diode rectifies the current induced in the antenna by the
microwaves. Rectenna are highly efficient at converting microwave energy
to electricity.
In laboratory environments, efficiencies above 90% have been
observed with regularity. In future rectennass will be used to generate
large-scale power from microwave beams delivered from orbiting SPS
satellites.
The sensor circuitry is a simple circuit, which detects if the
mobile phone receives any message signal. This is required, as the phone
has to be charged as long as the user is talking. Thus a simple F to V
converter would serve our purpose. In India the operating frequency of
the mobile phone operators is generally 900MHz or 1800MHz for the GSM
system for mobile communication.